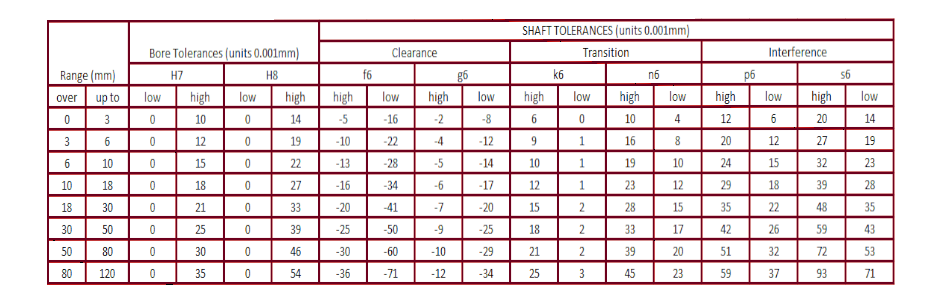
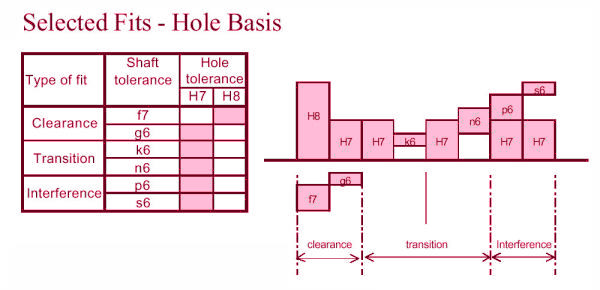
Bore and shaft tolerances
Bore and shaft tolerances are critical parameters for servomotors. Bore tolerance refers to the allowable deviation in the inner diameter of the motor’s mounting aperture, while shaft tolerance refers to the allowable deviation in the motor shaft’s diameter. These tolerances are essential to maintain the accuracy and precision of the motor’s movement and position control.
The bore and shaft tolerances directly impact the motor’s performance and longevity. If the bore or shaft tolerances are too loose, the motor’s mounting may become unstable, causing vibration and eventual failure. If the bore or shaft tolerances are too tight, interference fits can occur, leading to excessive heat and wear. Manufacturers typically specify the acceptable bore and shaft tolerances for their servomotors, and it’s important to follow these guidelines during installation and maintenance. Regularly checking these parameters can ensure that the servomotor maintains optimal performance and reliability.
The bore and shaft tolerances directly impact the motor’s performance and longevity. If the bore or shaft tolerances are too loose, the motor’s mounting may become unstable, causing vibration and eventual failure. If the bore or shaft tolerances are too tight, interference fits can occur, leading to excessive heat and wear. Manufacturers typically specify the acceptable bore and shaft tolerances for their servomotors, and it’s important to follow these guidelines during installation and maintenance. Regularly checking these parameters can ensure that the servomotor maintains optimal performance and reliability.
Below is a reference on bore and shaft tolerances corresponding to a given bore or shaft diameter:
Motor Technology will not accept any liability for the accuracy of the data supplied. This information is meant as a guideline only